Financial Accounting (FI) Module
Let’s Talk!
Overview
SAP FI is the finance module of SAP and comprises powerful tools and features. Businesses can benefit from the tool as it streamlines the organization’s financial ecosystem. Moreover, the tool is known to assist in making informed decisions. Thereby, helping the financial experts resolve most of the financial complications within the company.
What is SAP FI?: An Overview

SAP FI (Financial Accounting) is a module within the SAP ERP system that focuses on financial management and accounting processes. It is designed to meet the financial reporting and accounting requirements of organizations, providing a comprehensive suite of tools and functionalities to manage financial operations effectively.
The following are crucial aspects of FI:
- SAP FI keeps a complete audit trail of all corporate transactions, from financial statements to specific papers, and records them all.
- Sub-ledger account postings always result in a matching G/L account posting as well.
- Since the information is current, the entire organization has access to the financial accounting data.
- It provides the organization with operational knowledge and efficient decision-making.
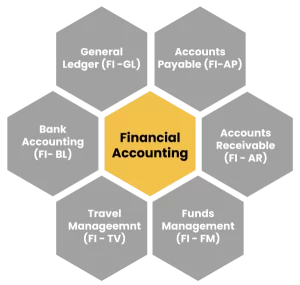
Inclusions of Modules
SAP FI is a comprehensive module within the SAP ERP system that covers various aspects of financial management and accounting. It consists of several sub-modules that work together to handle different financial processes.
General Ledger Accounting (FI-GL):
The General Ledger Accounting sub-module is at the core of SAP FI. It provides a central repository for maintaining account balances and supports functions such as journal entries, account reconciliation, and financial statement generation.
Accounts Payable (FI-AP):
The Accounts Payable sub-module deals with managing outgoing payments and liabilities to suppliers and vendors. It handles invoice processing, payment processing, vendor master data management, and so on.
Accounts Receivable (FI-AR):
The Accounts Receivable sub-module focuses on managing incoming payments and receivables from customers.
Asset Accounting (FI-AA):
Asset Accounting is responsible for managing fixed assets within an organization. It covers the entire lifecycle of assets.
Bank Accounting (FI-BL):
The Bank Accounting sub-module deals with managing bank transactions and bank master data. It supports functionalities such as bank statement processing, bank reconciliation, and cash management.
Travel Management (FI-TV):
Travel Management in SAP FI handles travel-related expenses and reimbursements within an organization. It streamlines the travel expense claim process, tracks travel expenses, and manages travel allowances.
Funds Management (FI-FM):
The Funds Management sub-module is used for budgeting and managing funds within an organization. It supports budget planning, commitment management, and fund availability tracking.
Special Purpose Ledger (FI-SL):
The Special Purpose Ledger sub-module provides additional flexibility for financial reporting. It allows organizations to create custom ledgers and define their own financial structures to meet specific reporting requirements.
These are the primary sub-modules within SAP FI, each catering to different aspects of financial management and accounting. SAP FI offers a comprehensive suite of functionalities to meet the diverse financial needs of organizations across industries.
10 Things to Consider While Implementing SAP FI

Implementing SAP FI (Financial Accounting) requires careful planning and consideration to ensure a successful implementation. Here are some key factors to consider during the implementation process:
- Project Scope: Clearly define the scope of your SAP FI implementation.
- Business Process Analysis: Conduct a thorough analysis of your existing financial processes and identify areas for improvement.
- Data Migration: Plan and execute a structured data migration strategy.
- Organizational Change Management: Communicate the benefits of SAP FI to stakeholders and involve key users in the implementation process.
- Configuration and Customization: This includes setting up company codes, charts of accounts, fiscal year variants, document types, and other relevant settings.
- Integration with Other Modules: Consider the integration of SAP FI with other modules, such as Controlling (CO), Materials Management (MM), and Sales and Distribution (SD).
- Reporting and Analysis: Configure financial reporting structures, such as financial statements, profit centers, cost centers, and internal orders.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Ensure that SAP FI implementation adheres to local legal and compliance requirements.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Develop a comprehensive testing plan to verify the functionality and accuracy of SAP FI.
Ongoing Support and Maintenance: Plan for ongoing support and maintenance of the SAP FI system. Establish a support structure, provide user training, and allocate resources to address user queries.
How can BPX Help Implement the FI Module?

Being one of the leading SAP FICO consultant firms, BPX can help companies improve their financial operations. With a thorough insight into the SAP FI implementation process, BPX effectively leverages the power of technology.
The following sections take us on a detailed tour of how the best mid-sized SAP consulting firm would implement the system. Let’s take a look:
As-Is Process
In SAP FI (Financial Accounting), the As-Is process refers to the existing or current state of financial processes within an organization. SAP consulting firms ensure implementation-specific processes within each module of SAP FI based on the organization’s requirements and industry.
Business Blueprint (Gap-Fit & To-be)/ SAP functional specification document
The Business Blueprint is a key phase in the implementation of SAP FI where the organization’s requirements and processes are documented.
Within the Business Blueprint phase, two important documents are created. These are the Gap-Fit Analysis and the To-Be Process Definition.
- Gap-Fit Analysis: During this analysis, the organization’s existing processes are compared with the standard functionalities offered by SAP FI. The purpose is to identify any gaps or differences between the current processes and the desired state.
- To-Be Process Definition/SAP Functional Specification Document: This document outlines the desired state of the organization’s financial processes within the SAP FI system. It serves as a blueprint for the configuration and development of the SAP system to meet the organization’s requirements.
Master Data Migration/ Item Master Configuration
Master Data Migration is an important aspect of implementing SAP FI that involves managing and setting up key data elements within the system. In the context of SAP FI, master data includes elements such as company codes, general ledger accounts, vendors, customers, and assets. BPX takes care of the end-to-end configuration.
System Configuration along with Customization
This step involves the setting up of SAP FI modules based on the company’s requirements. Top SAP consulting firms in India tailor the system based on the organization’s specific needs.
Configuration implies structuring financial accounting areas of the company. This could include a chart of accounts and posting periods. Customization implies adapting the system based on the company’s unique requirements.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
Once the system has been configured based on the needs of the business, it then moves forward with the process of UAT.
Go-Live Preparation
This stage involves using dummy data for evaluating the output of the system. Once a satisfactory result is obtained, it then moves towards the next stage.
Go-Live
This is the final stage when the system goes live. It is now ready for use by the managers and the concerned staff of the company. It is recommended that one opts for BPX ensuring all aspects are covered.
After Go-Live Support
There may be a few initial hiccups in the newly-implemented system; BPX shall extend all the essential and required support to handle these speed breakers.
SAP FI FAQs
Let’s run through some of the most commonly asked questions about SAP FI.
The organizational elements in SAP FI can be enlisted in the following manner:
- Company
- Company Code
- Business Area
- Credit Control Area
- Functional Area
- FM Area
- Segment
- Profit Center
FI and CO are two separate modules of SAP. The fundamental distinction between SAP’s FI (Financial Accounting) and CO (Controlling) modules relates to their organizational focus and function.
The CO module is concentrated on internal management accounting, cost control, and decision-making whereas the FI module is aimed towards external financial reporting and compliance.
A thorough document that defines the functional requirements for a software system or product is known as a functional specification document. From the viewpoint of the user, it specifies how the system should act and what it should be able to perform.
The SAP FI-MM (Financial Accounting – Materials Management) integration describes the smooth connectivity between the FI and MM modules inside the SAP ERP system. Businesses require proper recording and tracking of financial transactions connected to procurement and inventory management. FI-MM integration enables this synchronization of financial and material management activities.

