PTP : Plan to Produce
Let’s Talk!
Overview
Plan to Produce, or PTP is a term used to define the entire process framework and the steps involved in the production, manufacturing, and supply chain management ecosystem. Simply put, PTP in SAP refers to the overall process of planning, manufacturing, and producing goods or services in an organization or business. At a more detailed level, the key elements in the SAP plan to produce process are forecasting, production planning & scheduling, shop floor control and execution, and production cost management and reporting. At times, we also include other components like production quality control, WIP (Work in Progress) inventory management, and raw material procurement, supply, and distribution.
The plan to produce process in SAP refers to a series of integrated modules that encompass the end-to-end production planning and execution activities within an organization. Key stages covered in SAP PTP are demand management, production planning, procurement, manufacturing, and inventory management. Thus, the main goal of the PTP process in SAP is to align and optimize the entire production cycle, leading to efficient utilization of resources, and reducing costs from planning to delivery, while catering to consumer requirements.
How does SAP Plan to Produce work? What are the key factors in the implementation journey?
As mentioned earlier, in the PTP process in SAP, the first phase is that of planning. This involves the strategic analysis of historical data and market trends, to forecast future customer demand, for which a production roadmap is developed. This framework considers factors like available production capacity, lead times, and resource availability. Once this blueprint is finalized, it is converted into a detailed production schedule, specifying the product quantity and time when each of the products is to be produced.
The execution phase of SAP PTP involves the procurement of the necessary raw materials and initiation of the production process based on the schedule drawn up. Throughout the production process, quality control measures are adhered to, so that the final products meet the required quality standards. Finally, the finished products are distributed to customers or stored in inventory for further distribution. The entire PTP cycle in SAP can be summed up in the diagram below:
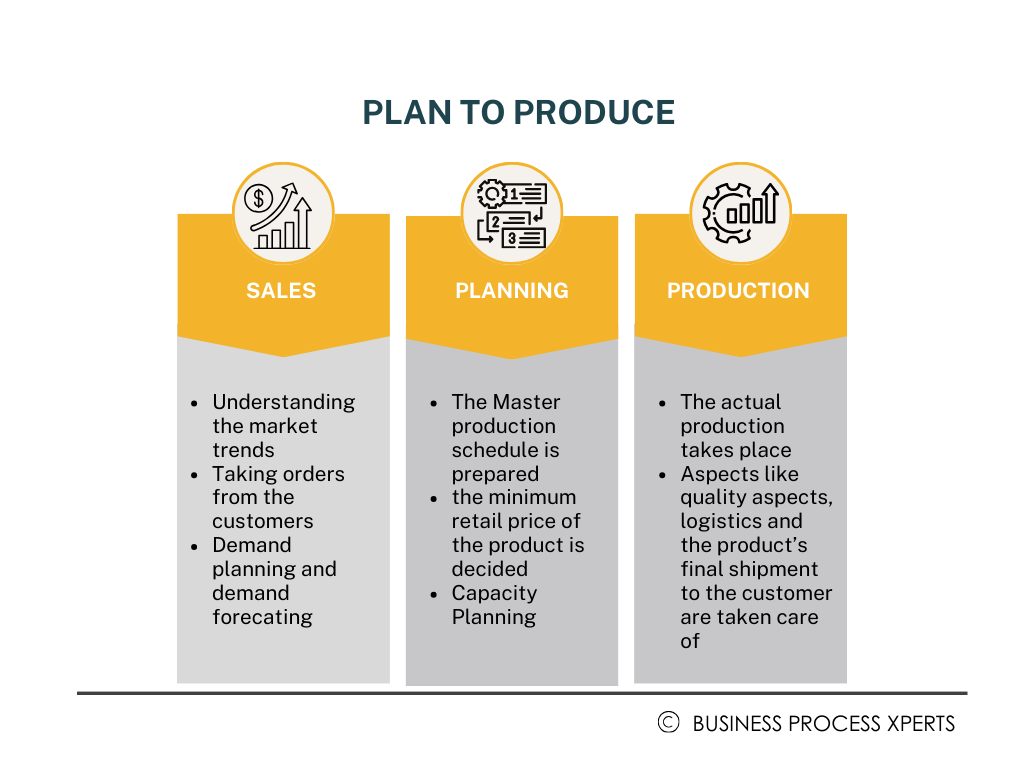
Please find below a general outline of how SAP plan to produce operates, and the key elements involved in the entire PTP process in SAP:
1)Product Definition: Here we clearly define the product to be produced, along with its specifications, attributes, and target market. This then serves as the building block for the entire production plan.
2)Resource Evaluation: The resources required for production are then assessed, including the raw materials, equipment, labor, and facilities. The availability, cost, and procurement options for each resource are also evaluated.
3)Production Process Development: An efficient, streamlined, and optimized production process flow is developed at this stage, taking into account factors like batch sizes, assembly methods, quality control checkpoints, and waste management. This involves breaking down the overall production into smaller, manageable steps.
4)Capacity Planning: Here, the production capacity needed to meet the forecast demand is determined. Elements like production rate, lead time, production cycles, and scalability are analyzed. Capacity planning helps to identify potential issues, challenges, and bottlenecks and also optimize the overall production schedule.
5)Supply Chain Management: This consists of setting up a robust supply chain to ensure a steady flow of raw materials and components, and also identifying suppliers and vendors, negotiating contracts, and establishing regular delivery schedules to minimize disruptions.
6)Production Scheduling: Developing a detailed production schedule is next on the cards, weighing in considerations such as resource availability, lead times, and customer demand. The production schedule is optimized and streamlined to minimize idle time and disruptions, reducing changeovers, and ensuring timely delivery.
7)Quality Control: This involves implementing quality control measures throughout the plan to produce process in SAP, as also establishing quality standards and benchmarks, inspection points, and testing procedures to ensure consistent product quality. The process followed here is iterative, flexible, and agile, consisting of continuous improvement and remedial measures.
8)Risk Assessment and Mitigation: This step addresses potential risks and challenges that could impact production. Contingency plans are developed to tackle supply chain disruptions, equipment breakdowns, labor shortages, or other unforeseen or emergency situations where production could come to a standstill.
9)Cost Management: The production costs are analyzed at each stage, with opportunities identified for cost optimization. Expenses pertaining to raw materials, labor, facilities, overheads, maintenance, and quality control are also continually tracked and monitored.
10)Continuous Improvement: In this stage, a process is established for monitoring and evaluating production performance. Feedback mechanisms are set up, and data is analyzed to identify areas for improvement, focus areas, streamline processes, and enhance the overall plan to produce SAP process.
In general, specific requirements for implementing the plan to produce process in SAP can differ, depending on the industry, market, product type, and specific attributes of the organization where the PTP in SAP is being executed or optimized.
While implementing a PTP cycle in SAP, it is crucial to maintain effective communication channels and manage various business departments and stakeholders. Progress has to be tracked and monitored in real-time, with a continuous need to adapt to changes and remain flexible and agile, ensuring that the SAP PTP masterplan aligns with the evolving needs of the market, industry, and business.
How will BPX help implement the Plan to Produce cycle in SAP?
The SAP Plan to Produce process framework encompasses all the activities required to transform raw materials into finished products, having under its ambit key components such as demand, resources, and cycle efficiency. It aims to streamline production processes, optimize resource allocation, and deliver products that fulfill customer requirements.
BPX can help you to successfully execute your SAP plan to produce implementation journey, expertly planning, and executing each step, with all the key stages and activities in the plan to produce cycle in SAP explained below:
1)As-Is Process:
This stage involves understanding and recording the current business processes in the PTP cycle in SAP. It consists of analyzing existing procedures and workflows. The following procedures can be considered under each process module:
- Demand Management: Analyzing current demand forecasting methods, data sources, and demand planning processes.
- Production Planning: Scrutinising the current, prevailing production planning processes, including production scheduling, capacity management, and material requirements planning (MRP).
- Procurement: Reviewing the current procurement framework, such as vendor management, purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and goods receipt.
- Manufacturing: Assessing the current methods and systems used for executing manufacturing processes, including shop floor control, production tracking, and quality management.
- Inventory Management: Analyzing the existing inventory management system, including stock control, material transportation, and inventory valuation.
2)Business Blueprint:
The Business Blueprint stage involves the creation of the future state or ‘To-Be’ processes based on the identified gaps between the ‘As-Is’ processes and the organization’s requirements. This stage includes the following activities:
- Fit-Gap Analysis: This consists of identifying the gaps between the ‘As-Is’ processes and the desired ‘To-Be’ processes, recording the requirements, and finding out the required system capabilities.
- To-Be Process Design: Here, we define the optimized SAP PTP processes based on the identified gaps and business requirements. This includes creating process flowcharts, defining roles and responsibilities, and documenting system requirements.
3)Master Data Migration/Item Master Configuration:
In this stage, the relevant master data, i.e., materials, vendors, and customers, is migrated or created in the SAP plan to produce process system. This includes tasks such as:
- Data Extraction: Taking out relevant data from the existing systems or sources.
- Data Cleansing: Reviewing and cleaning the extracted data to ensure accuracy, standardisation and consistency.
- Data Transformation: Converting the cleansed data into a format compatible with PTP in SAP and mapping it to the relevant categories.
- Data Migration/Creation: Loading the transformed data into the plan to produce process in SAP or creating new master data records directly in the new SAP system.
4)System Configuration/Realization:
The System Configuration/Realization stage involves configuring the SAP system based on the defined To-Be processes and requirements. It includes the following steps:
- Customization: Configuring the PTP in SAP to meet specific business requirements and process flows. This involves defining system settings, workflows, document types, authorization and access roles, and other relevant specifications.
- Integration: Configuring integration points between the various SAP modules and functionalities to ensure seamless data flow and process integration.
- Testing: Conduct unit testing to validate the configured system against the defined requirements and parameters, and fix any issues or bugs that may arise in the process.
5)User Acceptance Testing (UAT):
During the UAT stage, end-users test the configured SAP plan to produce system to ensure that it meets their needs and performs as expected. Key activities during UAT include:
- Test Case Preparation: Creating test scenarios and cases based on the defined processes, SOPs, and system requirements.
- Test Execution: Executing and implementing the test cases, recording results, and identifying any issues, anomalies, or errors.
- Issue Resolution: Collaborating with the implementation team to resolve any identified issues and retesting them to ensure their resolution and operationality.
6)Go-Live Preparation:
Based on the feedback received during UAT, necessary updates and improvements are made to the system. The Go-Live Preparation stage involves activities such as:
- Issue Resolution: Resolving and fixing any outstanding issues or gaps identified during UAT and ensuring that the system is functioning optimally.
- Data Migration: Finalizing the migration of master and transactional data from legacy systems to the plan to produce process in SAP.
- End-User Training: Holding regular training sessions to familiarize end-users with the new system and processes.
7)Go-Live:
The Go-Live stage involves transitioning and migrating from the old system to the PTP process in SAP for live operations and functionality. This includes:
- System Cut-Over: Moving from the existing system to the SAP system and ensuring a smooth transition with minimal disruptions.
- Post Go-Live Support: Providing prompt and regular support to users and addressing any issues, concerns, or bottlenecks that may crop up during initial system usage.
8)After Go-Live Support:
After the successful completion of the Go-Live stage, continuous support is provided to users to facilitate the smooth functioning of the plan to produce cycle in SAP. This consists of addressing user queries, resolving system issues, and continually optimizing the system in real-time based on user feedback.
BPX helps businesses successfully implement, execute, and optimize their end-to-end plan to produce cycle in SAP. It is key to understand here that a SAP plan to produce implementation and its associated activities may differ based on the organization’s specific needs, configuration, market standing, project scope, and the plan to produce SAP process methodology used.

All about BPX
Headquartered in Pune India, Business Process Experts (BPX) ranks amongst India’s leading process management consultants, specialising in tailored plan to produce SAP process solutions. The company was incorporated more than a decade back in 2012, and since then, it has witnessed a meteoric rise to become a market leader in the SAP PTP business process solutions ecosystem. BPX provides customized SAP plan to produce process blueprints for varied industry sectors like engineering, automobiles, banks, chemicals, garments and apparel, retail & hospitality, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, mining, ITeS, etc.
Helmed by an experienced team of engineers, management & finance experts, and SAP business process consultants, BPX and illustrious sister concerns like YRC have occupied pride of place as strategic, transformational partners for leading clients. As your trusted SAP consultant, BPX will guide you to align with the industry’s best practices, helping you reduce costs, utilize resources optimally and reap the rewards of an optimally functioning plan to produce SAP process. Our SAP business process experts will thoroughly analyze your organization’s plan to produce cycle in SAP and customize your entire PTP cycle in SAP, factoring in all your specific business requirements.
So, if you are a business owner or entrepreneur seeking to transform your organization’s PTP process in SAP, connect with BPX now. Our team will promptly get in touch with you to handhold you every step of the way in your unique PTP in SAP journey, helping your business grow, craft its own success story and stay well ahead of the curve!
FAQs
The Plan to Produce (PTP) process in SAP can be defined as the end-to-end business process framework that encompasses the planning and execution of production, manufacturing, and supply chain management activities within an organization. PTP generally includes key functional areas like demand management, production planning, procurement, manufacturing, and inventory management. The goal of the PTP process in SAP is to streamline and optimize the entire production cycle, resulting in efficient utilization of resources and reduced costs, while meeting customer demand.
The key stages or steps in the Plan to Produce (PTP) cycle in SAP are as follows:
- Demand management.
- Material Planning
- Production Planning
- Procurement and sourcing
- Manufacturing
- Inventory management
- Quality maintenance
- Sales, distribution, and delivery
The various benefits or advantages of implementing the plan to produce (PTP) business process can be given as under:
- Improved Production Planning Efficiency
- Accurate demand forecasting
- Efficient utilization of resources
- Reduction in overall costs
- Streamlined production process
- Greater quality control measures
- Risk assessment and mitigation
- Increased consumer satisfaction
- Enhanced visibility and reporting
- Greater co-ordination amongst departments
- Continuous process improvement
Procure to Pay (P2P) and Plan to Produce (PTP) are two separate business processes in the SAP framework, focusing on different aspects and stages in the supply chain. The Procure to Pay (P2P) process in SAP consists of the whole range of procurement and sourcing activities, starting from the initial process creation, requisition, vendor selection, purchase order creation, and order fulfillment, and ending with payment to suppliers. The Plan to Produce (PTP) process, on the other hand, includes the end-to-end production cycle, with its key elements and activities being demand management, production planning, procurement, manufacturing, inventory management, quality, sales, distribution, and delivery.

