FTD: Forecast to Delivery
Let’s Talk!
Overview
Forecast to Delivery or FTD in SAP can be defined as an all-encompassing end-to-end process that involves managing an entire product lifecycle for an organization or business, starting from the forecasting of product demand stage, production planning or procurement, right down to the delivery of the product to end customers. The forecast to delivery process in SAP refers to the customized process framework that integrates forecasting, planning, and delivery management within the overall SAP system.
The overarching goal of the FTD process in SAP is to ensure that customer demand is met effectively and optimally, along with the aligned production, inventory, and distribution systems. The FTD process ecosystem promotes collaboration among different business units, helping in eliminating bottlenecks and managing the supply chain consistently and efficiently.
How does the Forecast to Delivery cycle in SAP work? Phases during the implementation journey:
Here are the various steps involved in the forecast to delivery process in SAP:
1)Demand Forecasting: This step involves the prediction of future demand for products based on historical data, market and demand-supply trends, and other key factors. Businesses use forecasting to plan their production and inventory levels, and supply chain management activities optimally.
2)Sales & Demand Planning: Using the forecasted demand, organizations may strategize about the requisite quantities of each product to produce or procure. This involves aligning production schedules, procurement plans, and inventory levels with the anticipated or expected demand.
3)Production Planning: If the products are manufactured in-house or internally, the production planning process determines the quantities to be produced, the production schedule, and the allocation of resources to meet the forecast demand.
4)Procurement Planning: For products that are sourced externally, procurement activities are planned based on the forecasted demand. This involves placing orders with suppliers to ensure that the necessary raw materials or finished goods are available in optimum quantities, for production or resale.
5)Inventory Management: Throughout the forecast-to-delivery process, inventory levels are managed to ensure that products are readily available when needed. This involves tracking stock levels, replenishing inventory, and optimizing stock levels to avoid shortages or overstock situations.
6)Order Management: Once customers place orders for products, these orders are managed within the SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) process module. Orders are processed, scheduled for delivery, and notified and communicated to relevant departments for order fulfillment.
7)Order Delivery Planning: Delivery planning involves determining the most efficient way to fulfill customer orders. This includes selecting the appropriate shipping method, preparing the products for delivery, and scheduling delivery routes that are economical or cost-effective.
8)Order Delivery Execution: Products are physically shipped or delivered to customers according to the planned schedule. This step involves coordinating and orchestrating logistics, managing transportation schedules, and ensuring that products reach customers in prime condition and in accordance with pre-specified timelines.
9)Transparent & Clear Customer Communication: Throughout the process, clear and transparent communication with customers is crucial. Timely updates about order status, shipping notifications, and delivery confirmation keep customers informed in real-time, and maximize their product buying experience.
The various stages in SAP Forecast to Delivery process framework can be visualized through the following diagram, given below:
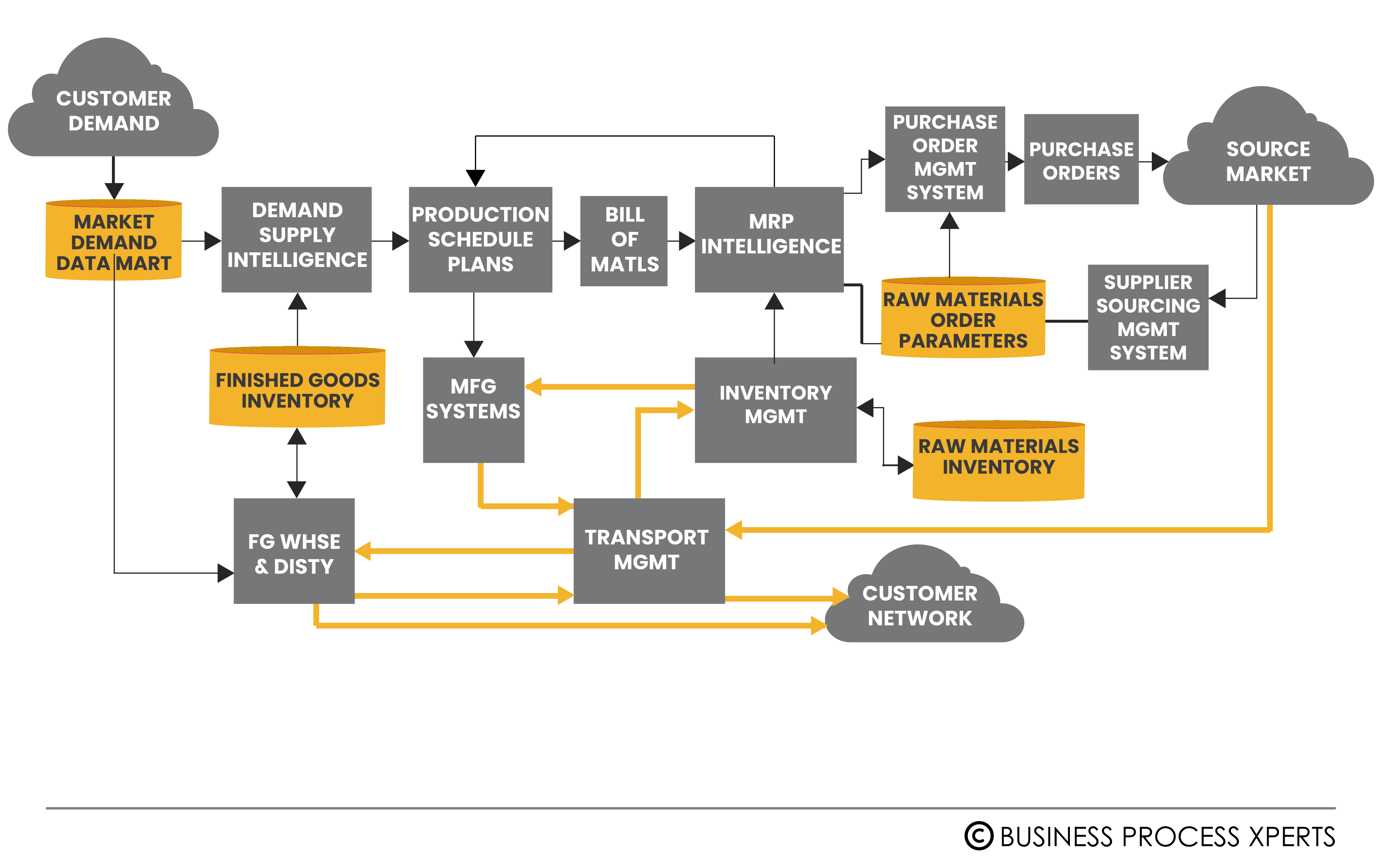
How will BPX help implement the Forecast to Delivery cycle in SAP?
It is the constant endeavour of BPX to guide and handhold you every step of the way to successfully plan, tailor and execute your FTD process in SAP, ensuring a smooth, hassle-free transition to the new system, and effectively solving and taking care of any issues, roadblocks, challenges, or bottlenecks along the way. Implementing the Forecast to Delivery (FTD) cycle in SAP consists of a series of steps to streamline the entire product lifecycle and product management process, from forecasting demand to customer product delivery.
Below is an analysis of each of these SAP FTD phases:
- As-Is Process:
The ‘As-Is’ Process phase involves the documentation of the existing processes and procedures related to the SAP Forecast to Delivery cycle. This provides a clear understanding of the current state of operations in the product lifecycle. Procedures under this phase could consist of:
- Documenting the current process of demand forecasting.
- Detailing the steps involved in order management, production planning, procurement, inventory management, and final delivery.
- Identifying pain points, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement in the current processes used.
- Business Blueprint (Fit-Gap & To-Be):
In the Business Blueprint phase, we define the future state (To-Be) processes based on industry best practices and the gaps identified in the ‘As-Is’ process. This involves:
- Mapping out the ideal forecast to delivery process in SAP.
- Identifying areas where standard functionalities in the FTD cycle in SAP help to align the business requirements (Fit) and areas where customizations or third-party integration is needed (Gap).
- Creating process flow and data flow diagrams and specifying integration points between the various SAP modules (e.g., SD, MM, PP).
- Master Data Migration/Item Master Configuration:
This phase involves setting up the core master data that is essential for the SAP Forecast to Delivery process. This includes the following:
- Defining product master data, including product codes, descriptions, units of measurement, etc.
- Creating customer master data for order processing and delivery.
- Establishing material types, pricing, and relevant attributes.
- System Configuration / Realization (as per To-Be) along with Customization:
In this phase, the FTD process in SAP is configured according to the ‘To-Be’ processes defined in the FTD in SAP Business blueprint. This includes:
- Configuring settings for demand forecasting based on chosen SAP modules (e.g., IBP – Integrated Business Planning or APO – Advanced Planning & Optimisation).
- Customizing the SD module for order processing, pricing, and delivery scheduling.
- Configuring the MM module for procurement and inventory management as per ‘To-Be’ requirements.
- Integrating various modules to ensure seamless data flow.
- UAT (User Acceptance Testing):
During UAT, end-users test the configured FTD cycle in SAP to ensure that it meets the defined and specified requirements. Steps within this phase include:
- Creating test scenarios that replicate real-world scenarios of demand forecasting, order processing, and delivery.
- Executing tests to verify the system’s accuracy, usability, and performance.
- Identifying and resolving any issues or discrepancies discovered or diagnosed during testing.
- Go-Live Preparation (Update as per feedback during UAT):
Based on UAT feedback, we make necessary adjustments to the system and documentation. This includes:
- Addressing and resolving issues identified during UAT.
- Updating process documentation, SOPs, user manuals, and training materials.
- Go-Live:
During the crucial Go-Live phase, the forecast to delivery cycle in SAP is finally launched to commence live operations. Key activities here include:
- Transitioning from the old process to the new FTD in SAP based process.
- Monitoring and tracking the initial stages of live operations to ensure smooth functioning, without any potential disruptions.
- Providing continuous support to users and addressing any immediate issues.
- After Go-Live Support:
After the system is live, ongoing system support and maintenance are critical after the commencement of operations. Activities in this stage include:
- Providing user training and support as they adapt to the new system.
- Addressing any post-go-live issues, challenges, configuration queries, or optimizations.
- Continuously monitor system performance and make adjustments as and when needed.

BPX – An Overview
Based out of Pune India, Business Process Experts (BPX) is a market leader in the business process solutions landscape, offering unique, customized SAP FTD solution offerings to its discerning customers. With offices located in UAE and other prominent Indian cities, the company was initially established in 2012. Since then, it has taken giant strides, growing steadily over the years to become a key player in the SAP forecast to delivery space.
Run by a professional team with diverse industry expertise, BPX and its renowned sister concern YRC are key strategic, transformational partners for top-tier clients worldwide. The company’s distinguished client base belongs to leading industry sectors like engineering, automobiles, banks, chemicals, garments and apparel, retail & hospitality, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, mining, and ITeS.
BPX will expertly tailor the implementation of the forecast to delivery process in SAP with the client’s unique business requirements, taking care of the associated pain points, issues, and challenges. Their SAP FTD business process experts will collaborate with you to draw up an effective forecast to delivery cycle in SAP process roadmap, which will focus on optimal system performance, proper streamlining of business processes, and overall cost reduction, a win-win for your business.
Hence, if you are an ambitious business owner and entrepreneur looking to transform your organization’s FTD cycle in SAP, your search ends here, connect with BPX now. Our team will promptly connect with you to craft your unique SAP FTD success story, helping you achieve your true business potential, and ensuring that you always stay well ahead of your competitors!
FAQs
In SAP, the Forecast to Delivery (FTD) process refers to end-to-end business product lifecycle management, that encompasses forecasting customer demand, planning production or procurement, and finally delivering the products to customers. This process integrates various components and modules within SAP, i.e., Sales and Distribution (SD), Materials Management (MM), and Production Planning (PP), to ensure that products are produced or procured in the right quantities, at the right production costs, and delivered to customers on time.
The various steps in the forecast to delivery cycle in SAP can be outlined below:
- Demand Forecasting
- Sales & Operations Planning
- Production Planning
- Materials Procurement Planning
- Order Processing
- Production Delivery & Execution
- Procurement Execution
- Good Receipt (GR) & Order Fulfillment
- Invoicing & Payment
- Reporting & Analysis
The Forecast to Delivery (FTD) process in SAP seeks to make sure that customer demand is effectively met, along with the alignment and optimization of production, inventory, and distribution processes. The FTD process framework promotes effective collaboration among different business departments and helps in eliminating related issues and challenges, leading to an efficient management of the supply chain.
Implementing the Forecast to Delivery (FTD) process in SAP offers several key benefits and advantages to businesses, namely:
- Improved customer satisfaction
- Efficient resource utilization
- Better resource & production planning and decision-making
- Reduced lead times for production & procurement
- Optimized inventory levels and reduced wastage result in cost savings
- Enhanced collaboration between different business departments
- Accurate inventory management
- Mitigation of demand variability through advanced forecasting techniques and analytics
- Increased real-time visibility into various stages of the FTD process
- Data-driven insights
- Flexibility and adaptability to market changes
- Statutory compliance and regulatory adherence
- Standardized process governance
- Scalability & continuous improvement:
Therefore, implementing the forecast to delivery process in SAP helps organizations to achieve greater operational efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction by aligning and integrating demand, production, and delivery processes, while leveraging real-time data-driven insights and decision-making.
Forecast to Delivery (FTD) and Plan to Produce (PTP) are two distinct SAP business processes, impacting different aspects of the supply chain. While forecast to delivery covers a broader range of production-related activities across the entire supply chain from forecasting to delivery, plan to produce specifically addresses the production planning and execution phases. Both these processes are integral to the management of different aspects of the supply chain within an organization’s SAP process implementation journey.

