PTP : Procure to Pay/ Procure to Pay (P2P) OR Invoice to Payment (I2P)
Let’s Talk!
Overview
As enterprises look for new ways to cut cost spirals and control spending, the sourcing and procurement procedures encompassing the P2P cycle in SAP are being increasingly scrutinized. The procure to pay process in SAP, also termed as purchase to pay or P2P, essentially refers to the cycle of acquiring, paying, and accounting for goods or services which are key to running a business optimally, based on specified milestones and timelines and for a reasonable price.
The P2P process in SAP is a subset of the larger procurement management ecosystem and consists of integrating the purchasing and accounts payable systems to create optimal efficiencies. Invoice to Payment (I2P) on the other hand, is the introductory step in the procure to pay cycle in SAP. The I2P process focuses more on activity streamlined to manage supplier payments. The request for payment for supplier goods or services is covered under Invoice to Pay.
How does SAP Procure to Pay work?
The P2P cycle SAP process flow can be explained through this diagram given below:
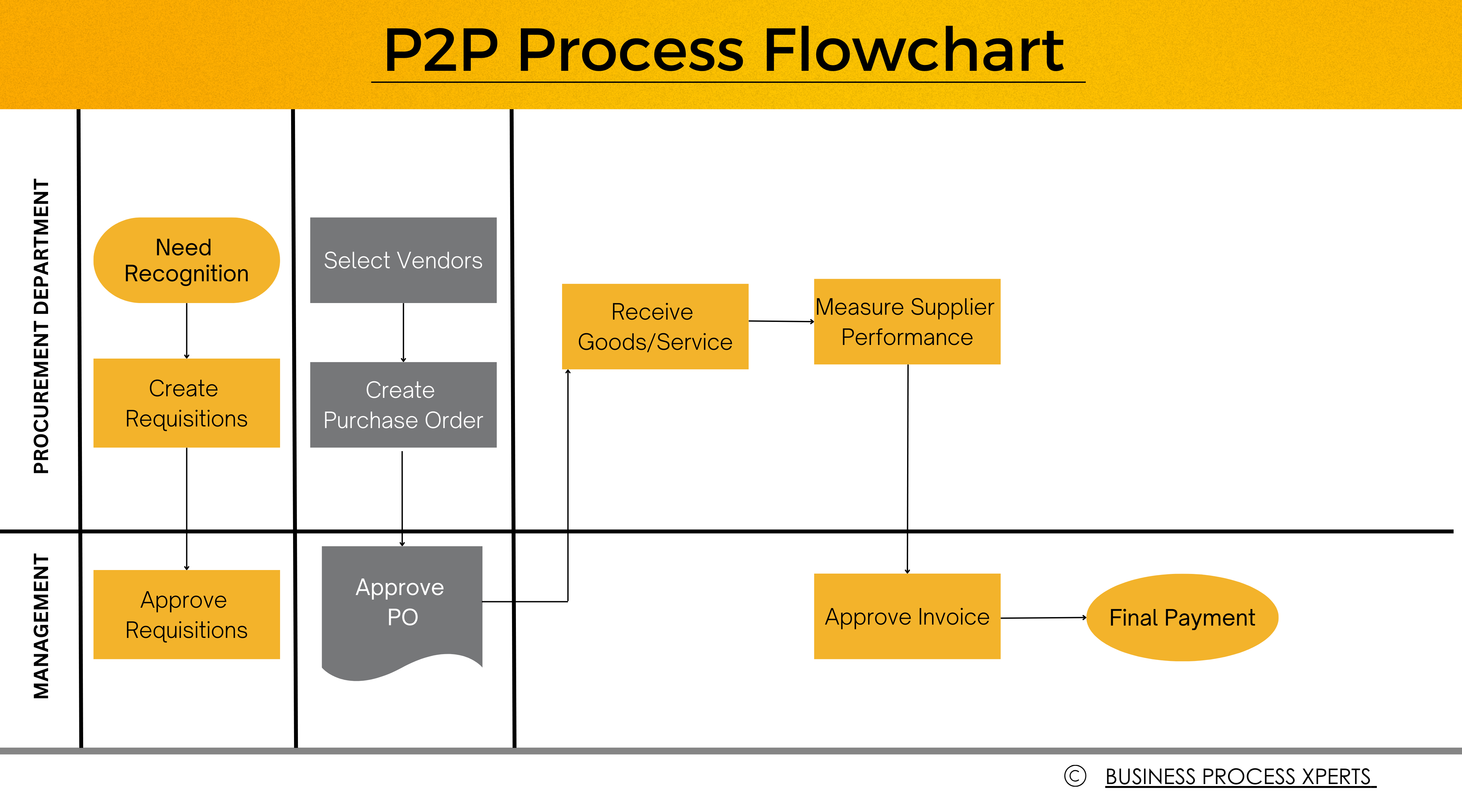
Here are the key steps involved in implementing the P2P cycle in SAP:
1)Create Process Definitions: Create company codes for purchasing organizations and various groups. Define vendor/supplier and material master records (for goods & services), plant, storage locations, other general information, payment terms, and banking details.
2) Create and approve (Purchase) Requisition & RFQ (Request for Quotation): Create and approve a purchase requisition for the required goods or services, specifying the material, quantity, delivery date, and account assignment. Subsequently, an RFQ (Request for Quotation) should be created to invite suppliers to submit their quotations or competitive bids. RFQ details such as validity period, terms, and conditions must be also maintained and updated.
3)Vendor Selection and Purchase Order (PO): In this P2P cycle SAP, quotations for various vendors must be evaluated and compared based on the criteria laid down in the RFQ document, and the vendor(s) are finally selected.
4) Create & Approve Purchase Order: The next step is to create and approve the Purchase Order (PO), specifying PO details like the material, quantity, pricing, and delivery schedule. The PO is a legally binding document between the organization and the vendor.
5)Order fulfillment & Goods Receipt (GR): Goods & Services are received against the PO. A Goods Receipt (GR) is then created and cross-checked in the SAP system to update stock quantities and valuation. The GR regularly updates the inventory and triggers subsequent processes (like quality control checks and inspection) and verifies the completeness and correctness of the order delivery.
6) Measure supplier performance & invoice verification (IV) & approval: After the vendor sends the invoice, it must be approved and verified against the purchase order and goods receipt, and the supplier’s performance evaluated. In SAP Procure to Pay, the invoice undergoes three-way tallying (with the PO, GR, and invoice) to verify the quantities, prices, and terms & conditions, to ensure accuracy, and to approve and validate the payment. The invoice is then saved and entered in the records and posted, after which we process payments to the vendor.
7) Final Payment Processing: After the payment terms and payment methods are configured in SAP Procure to Pay, the payment proposals are generated, and the final payment amount is processed for the vendor.
These steps provide a step-by-step guide to the Procure to Pay cycle in SAP. We at Business Process Experts(BPX) are seasoned SAP implementation consultants, who can expertly evaluate your organization’s SAP version and configuration, and customize a tailor-made solution just for you based on your business requirements and needs.
How will BPX help implement the Procure to Pay cycle in SAP?
BPX can help execute the entire Procure to Pay (P2P) cycle in SAP, planning and implementing each stage of the implementation process, as given below:
1) As-Is Process:
- Understand and document all the current, relevant procurement processes in the P2P cycle in SAP, including the procedures followed within each process (e.g., PR creation, RFQ, PO creation, Goods Receipt, invoice verification, payment processing, etc.).
- The main objective of the As-Is business process is to provide a template for identifying areas for improvement and pain points in the current processes, and optimizing the use of resources, leading to an overall increase in efficiency and productivity.
2) Business Blueprint (Fit-Gap & To-be):
- Conduct workshops and assimilate business requirements for the future state (To-Be) processes.
- Analyze the differences and gaps between the As-Is and To-Be processes and lay down the necessary solutions, changes, and improvements.
- Document the business blueprint, which outlines the proposed changes, consisting of the process flow, system requirements, and integration points.
- Perform a Fit-Gap analysis: A fit-gap analysis is a flexible method that diagnoses gaps in process functionalities when operating or business requirements of the organizations are compared with its corresponding system capabilities.
3) Master Data Migration/Item Master Configuration:
- Define the requisite master data elements, like vendor master data, material master data, and purchasing information data.
- Migrate existing master data into the procure to pay process in SAP or set up new master data as per the defined parameters.
- Configure the item master settings, including material types, valuation classes, and pricing conditions.
4) System Configuration/Realization:
- In the P2P cycle SAP, the system must be tailored based on the defined To-Be processes.
- Configure system settings, document types, number ranges, and field selections for PRs, POs, GRs, invoices, and final payment processing.
- Establish and create workflow rules for approval processes.
- Define integration points with other SAP modules like Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO).
- Develop any required customization or enhancements to cater to specific business needs.
5)User Acceptance Testing (UAT):
- Create and execute diverse UAT scenarios to validate the configured P2P process in SAP.
- Engage end-users to test the system functionalities, and perform end-to-end testing, suitably identifying any specific issues, gaps, or concerns.
- Document and address any identified issues or gaps during the UAT phase.
6) Go-Live Preparation:
- Update the system configuration based on the feedback and issues identified during UAT.
- Conduct end-user training to ensure familiarity with the new SAP procure to pay processes and system.
- Develop activities like data migration, open item clearing, and system readiness checks.
- Prepare an extensive go-live plan, including the sequence of activities, timelines, and milestones.
7)Go-Live:
- Plan & execute the go-live plan and subsequent transition to the live SAP system.
- Begin using the new P2P cycle in SAP in the new production environment from the earlier testing (sandbox) environment.
- Monitor system performance and address any immediate issues or concerns.
8)After Go-Live Support:
- Provide post-go-live support to end-users, answering any questions or issues that may arise.
- Monitor system performance, identify areas for further improvements and optimization, and continually make necessary adjustments.
Conduct periodic reviews to assess the effectiveness of the implemented P2P process in SAP and address any ongoing challenges or improvements to be made.
The procure to pay cycle in sap is an agile, iterative process that requires close alignment and collaboration between business process consultants, stakeholders, SAP consultants, and IT & procurement teams. Throughout the P2P cycle SAP, modules such as Materials Management (MM), Financial Accounting (FI), and Controlling (CO) are aligned and integrated to provide end-to-end visibility and control over the entire procurement and payment mechanism. The SAP system helps to automate and streamline these processes, improving efficiency, reducing manual effort, lowering costs, and providing accurate financial data for audits, governance control, reporting, and analysis.
About BPX

Headquartered in Pune India, Business Process Experts (BPX) is one of India’s premier management consultants offering customized solutions focusing on the procure to pay process in SAP. Ever since its inception in 2012, BPX has transformed the SAP process solutions landscape by providing industry-ready processes for diverse businesses and sectors, whether it is automobile or engineering, banks or financial institutions, and retail or manufacturing.
Led by experienced SAP implementation professionals, BPX and its sister organizations like YRC have been strategic and transformational partners for top-tier clients for several years now, expertly guiding clients on the nuances of implementing a P2P process in SAP. As your trusted SAP business process consultant, BPX can help you to follow the industry’s best practices, thereby ensuring a successful implementation.
If you are a business owner or entrepreneur looking to implement a successfully orchestrated, digitized, and automated procure to pay process in SAP, look no further, and connect with BPX now. We will first understand your exact business requirements and then suitably customize your process timeline. We will then tailor specific steps in the P2P process in SAP according to your organization’s specific requirements, scope, and system landscape, thus helping you to maximize your true business potential, and grow exponentially to stay well ahead of the curve!
FAQs
The procure to pay cycle in SAP, also known as Purchase to Pay or P2P, is the full series of steps and actions that a business engages in when they procure, pay & remit money for goods or services sourced from an external supplier. The process is an active part of the larger procurement management ecosystem and consists of integrating the purchasing and accounts payable systems to create optimal efficiencies.
The procure to pay process in SAP involves four broad stages:
- Selecting the vendor, and goods and services
- Implement the compliance and order process
- Goods receipt and reconciliation
- Final Invoicing and payment
Procure-to-Pay, also referred to as Purchase-to-Pay or P2P consists of these key processes in the procurement lifecycle: requisitioning, purchasing, receiving, invoicing, and paying for goods and services. Thus, the P2P cycle in SAP comprises all the steps involved in receiving and paying for goods or services.
The key benefits of the procure to pay (P2P) process are:
- Streamline the procurement process by using digital, automated processing software.
- Reduce invoice processing costs by going paperless.
- The automated P2P process saves time and costs, reduces risks, and enhances the overall efficiency, financial controls, and governance.
- Get total visibility into the supply chain, with both buyers and suppliers able to view the invoice status in real-time.
- Invoice and process exceptions can be managed quickly and efficiently.
- Improve buyer-supplier relationships and deal negotiations.
- Efficient P2P solutions capture real-time, historical, and on-demand reporting data, enabling quicker decision-making.
The various detailed steps in the procure to pay (P2P) process cycle are:
- Identification of requirement
- Authorization of Purchase Requisition/Purchase Request (PR)
- Final approval of PR/Role of inventory controller
- Procurement
- Identification of supplier(s)/vendor(s)
- Floating of Request for Proposal (RFP)/Request for Quotation (RFQ)
- Receipt of technical quotations & their evaluation
- Receipt of commercial quotations & negotiation
- Selection of vendor and award of the final contract
- Purchase Order (PO) creation and acknowledgment
- Creation of advanced shipment note (ASN)
- Good Receipt (GR)
- Invoice tallying and recording
- Final payment to supplier

